20 Most commonly used JavaScript Scenarios with Sample code Snippet in Form Script Dataverse/ Dynamics 365 CE

JavaScript is a powerful tool when working with Dataverse (formerly known as Common Data Service) and Dynamics 365 Customer Engagement (CE). It allows developers to create custom functionalities, validate data, and enhance user interactions. Below, we’ll explore some of the most commonly used JavaScript scenarios with sample code snippets to help you get started.
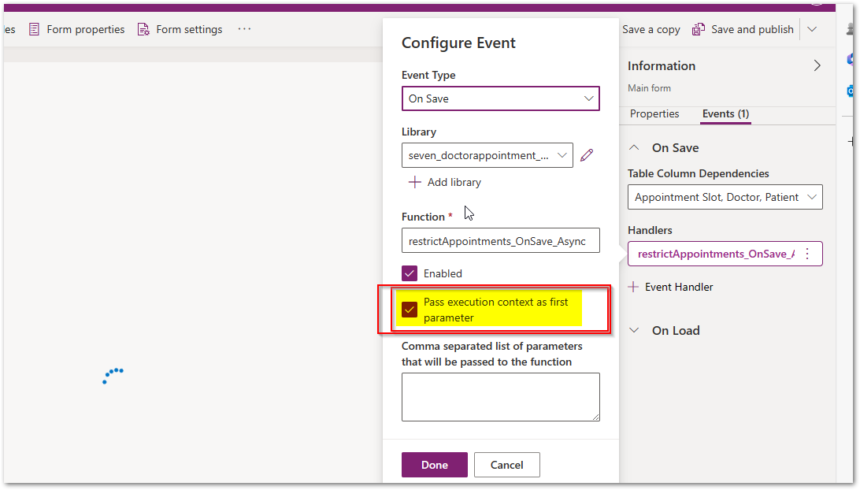
For all this script, you need to pass execution Context parameter from Event handler. Same screenshot given below.
1. Form Load Event
When a form is loaded, you might want to perform certain actions such as setting default values, hiding/showing fields, or pre-filling data. Here’s how you can do it:
function onLoad(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
// Set the default value of a field
formContext.getAttribute("new_fieldname").setValue("Default Value");
// Hide a section
formContext.ui.tabs.get("tabname").sections.get("sectionname").setVisible(false);
}
2. Form Save Event
You might want to execute JavaScript before a form is saved to validate data or prevent the save operation under certain conditions.
function onSave(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var fieldValue = formContext.getAttribute("new_fieldname").getValue();
if (fieldValue === null || fieldValue === "") {
// Prevent save and alert user
executionContext.getEventArgs().preventDefault();
alert("The field cannot be empty.");
}
}
3. Field OnChange Event
Triggering JavaScript when a field value changes can be useful for dynamic form behaviors like validation or auto-populating related fields.
function onFieldChange(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var fieldValue = formContext.getAttribute("new_fieldname").getValue();
if (fieldValue !== null && fieldValue !== "") {
// Perform some action
formContext.getAttribute("new_relatedfield").setValue("Calculated Value");
}
}
4. Show/Hide Fields Based on Another Field’s Value
Sometimes, you need to show or hide fields dynamically based on the value of another field.
function toggleFieldVisibility(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var toggleValue = formContext.getAttribute("new_togglefield").getValue();
var targetField = formContext.getControl("new_targetfield");
if (toggleValue === "Nice") {
targetField.setVisible(true);
} else {
targetField.setVisible(false);
}
}
5. Setting Field Requirement Levels
Adjusting the requirement level of a field based on other data inputs can help ensure data integrity.
function setFieldRequirement(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var status = formContext.getAttribute("statuscode").getValue();
var targetField = formContext.getAttribute("new_targetfield");
if (status === 100000000) { // Assuming 100000000 is a specific status value
targetField.setRequiredLevel("required");
} else {
targetField.setRequiredLevel("none");
}
}
6. Filtering Lookup Fields using FetchXML
Filtering lookup fields based on another field’s value can create a more streamlined user experience by presenting relevant options only.
function filterLookup(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var dependentFieldValue = formContext.getAttribute("new_dependentfield").getValue();
var lookupControl = formContext.getControl("new_lookupfield");
if (dependentFieldValue !== null) {
lookupControl.addPreSearch(function() {
var fetchXml = "<filter type='and'>" +
"<condition attribute='new_relatedfield' operator='eq' value='" + dependentFieldValue + "' />" +
"</filter>";
lookupControl.addCustomFilter(fetchXml);
});
}
}
7. Auto-Populate Fields Based on Lookup Selection
Auto-populating fields based on the value selected in a lookup field can save users time and reduce data entry errors.
function onLookupFieldChange(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var lookupValue = formContext.getAttribute("new_lookupfield").getValue();
if (lookupValue !== null) {
// Assuming the lookupValue is an array with the first element containing the selected entity's details
var lookupId = lookupValue[0].id;
// Fetch related data using Web API
Xrm.WebApi.retrieveRecord("relatedentity", lookupId, "?$select=new_relatedfield1,new_relatedfield2").then(
function success(result) {
formContext.getAttribute("new_field1").setValue(result.new_relatedfield1);
formContext.getAttribute("new_field2").setValue(result.new_relatedfield2);
},
function error(error) {
console.log(error.message);
}
);
}
}
8. Display Notifications
Displaying notifications on a form can alert users to important information or guide them through processes.
function displayNotification(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var fieldValue = formContext.getAttribute("new_fieldname").getValue();
if (fieldValue < 0) {
formContext.ui.setFormNotification("The value cannot be negative.", "ERROR", "1");
} else {
formContext.ui.clearFormNotification("1");
}
}
9. Manipulating Subgrids
Manipulating subgrids can enhance the user experience by dynamically adding or removing records or modifying their appearance based on conditions.
function manipulateSubgrid(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var subgridControl = formContext.getControl("new_subgrid");
subgridControl.addOnLoad(function() {
var subgridRows = subgridControl.getGrid().getRows();
subgridRows.forEach(function(row) {
var rowData = row.getData().getEntity();
var columnValue = rowData.attributes.get("new_columnname").getValue();
if (columnValue === "SpecificValue") {
// Perform some action, e.g., highlight the row
row.getCell("new_columnname").setBackgroundColor("#FF0000");
}
});
});
}
10. Working with Business Process Flows
JavaScript can interact with business process flows to dynamically change stages, set values, or validate steps.
function onStageChange(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var process = formContext.data.process;
process.addOnStageChange(function() {
var activeStage = process.getActiveStage();
var stageName = activeStage.getName();
if (stageName === "Specific Stage") {
formContext.getAttribute("new_fieldname").setValue("Value for specific stage");
}
});
}
11. Working with Async Save Operation & Prevent Save Opearation using Async and Await
If you want to prevent save operation on save event using some validation with async methods such as Xrm.WEB API below is a code snippet.
NOTE : Make sure to enable Async OnSave Feature in Model Driven APP.
async function restrictAppointments_OnSave_Async(executionContext) {
try {
// This method ensures that if an error occurs during the save event,
// the save operation will be prevented. This helps maintain data integrity
// by not allowing the save to proceed when there are errors in the script.
executionContext.getEventArgs().preventDefaultOnError();
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var doctorSelected = formContext.getAttribute("seven_doctor").getValue();
var patientSelected = formContext.getAttribute("seven_patient").getValue();
var appointmentSlot = formContext.getAttribute("seven_appointmentslot").getValue();
// Ensure all required values are present
if (!doctorSelected || !doctorSelected[0] || !patientSelected || !patientSelected[0] || !appointmentSlot) {
formContext.ui.setFormNotification("Doctor, patient, and appointment slot are required fields.", "ERROR", "REQUIRED_FIELDS");
throw new Error("Doctor, patient and slot is required.");
}
var doctorID = doctorSelected[0].id;
var patientID = patientSelected[0].id;
var year = appointmentSlot.getFullYear();
var month = appointmentSlot.getMonth() + 1;
var day = appointmentSlot.getDate();
var appointmentSlotValue = `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
var fetchXML = `
<fetch version='1.0' mapping='logical' no-lock='false' distinct='true'>
<entity name='seven_doctorappointment'>
<attribute name='statecode'/>
<attribute name='seven_doctorappointmentid'/>
<attribute name='seven_name'/>
<attribute name='createdon'/>
<attribute name='seven_appointmentnumber'/>
<attribute name='seven_appointmentslot'/>
<attribute name='seven_doctor'/>
<attribute name='seven_patient'/>
<order attribute='seven_appointmentnumber' descending='false'/>
<order attribute='seven_appointmentslot' descending='false'/>
<attribute name='statuscode'/>
<filter type='and'>
<condition attribute='statecode' operator='eq' value='0'/>
<condition attribute='seven_doctor' operator='eq' value='${doctorID}' uitype='systemuser'/>
<condition attribute='seven_patient' operator='eq' value='${patientID}' uitype='contact'/>
<condition attribute='seven_appointmentslot' operator='on' value='${appointmentSlotValue}'/>
</filter>
</entity>
</fetch>`;
var fetchXmlFinal = `?fetchXml=${encodeURIComponent(fetchXML)}`;
let result = await Xrm.WebApi.retrieveMultipleRecords("seven_doctorappointment", fetchXmlFinal);
var notificationID = "MYMSG";
if (result.entities.length >= 2)
throw new Error("You cannot create more than 2 appointments for the same patient and doctor on the same day.");
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error in restrictAppointments_OnSave_Async:", error.message);
throw error;
}
}
12. Working with XML HTTP to fetch records on Save and validate restrict save
In this example it shows how to use XML HTTP call to read records from server on save and validate with return result and restrict save operation if validation failed.
function restrictAppointments(executionContext)
{
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var doctorSelected = formContext.getAttribute("seven_doctor").getValue();
var doctorID = doctorSelected[0].id;
var patientSelected = formContext.getAttribute("seven_patient").getValue();
var patientID = patientSelected[0].id;
var appointmentSlot = formContext.getAttribute("seven_appointmentslot").getValue();
var year = appointmentSlot.getFullYear();
var month = appointmentSlot.getMonth()+1;
var day = appointmentSlot.getDate();
var appointmentSlotValue = year+"-"+month+"-"+day;
var fetchXML ="<fetch version='1.0' mapping='logical' no-lock='false' distinct='true'><entity name='seven_doctorappointment'><attribute name='statecode'/><attribute name='seven_doctorappointmentid'/><attribute name='seven_name'/><attribute name='createdon'/><attribute name='seven_appointmentnumber'/><attribute name='seven_appointmentslot'/><attribute name='seven_doctor'/><attribute name='seven_patient'/><order attribute='seven_appointmentnumber' descending='false'/><order attribute='seven_appointmentslot' descending='false'/><attribute name='statuscode'/><filter type='and'><condition attribute='statecode' operator='eq' value='0'/><condition attribute='seven_doctor' operator='eq' value='"+doctorID+"' uitype='systemuser'/><condition attribute='seven_patient' operator='eq' value='"+patientID+"' uitype='contact'/><condition attribute='seven_appointmentslot' operator='on' value='"+appointmentSlotValue+"'/></filter></entity></fetch>";
console.log(fetchXML);
var fetchXmlFinal = encodeURI(fetchXML);
var query = "/api/data/v9.2/seven_doctorappointments?fetchXml="+fetchXmlFinal;
var globalContext = Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext();
var finalpathwithquery = globalContext.getClientUrl() + query;
var data = null;
var isAsync = false;
var req = null;
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
req = new XMLHttpRequest();
}
else if (window.ActiveXObject) {
req = new ActiveXObject("MSXML2.XMLHTTP.3.0");
}
req.open("GET",finalpathwithquery,isAsync);
req.setRequestHeader("OData-MaxVersion", "4.0");
req.setRequestHeader("OData-Version", "4.0");
req.setRequestHeader("Accept", "application/json");
req.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8");
req.setRequestHeader("Prefer", "odata.include-annotations=\"*\"");
req.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (this.readyState === 4) {
req.onreadystatechange = null;
if (this.status === 200) {
var result = JSON.parse(this.response);
data = result;
}
else {
Xrm.Utility.alertDialog(this.statusText);
}
}
};
req.send();
if(data.value.length >=2)
{
Xrm.Utility.alertDialog("You cannot create more than 2 apppointments for same patient and same doctor on same date. There are total "+data.value.length+ " records retrieved");
executionContext.getEventArgs().preventDefault();
}
}13. Show Confirm Dilog on Command Button Click and update record status on confirmation and form refresh using Async Xrm.WEBAPI Calls
HereThis example shows how to Show Confirm Dilog on Command Button Click and update record status on confirmation and form refresh using Async Xrm.WEBAPI Calls
async function markExpired(formContext)
{
var confirmStrings = { text:"Are you sure to mark this medicine Expired?",
title:"Expire Dialog" };
var confirmOptions = { height: 200, width: 450 };
Xrm.Navigation.openConfirmDialog(confirmStrings, confirmOptions).then(
async function (success) {
if (success.confirmed)
{
// change medicine status to expired
// define the data to update a record
var data =
{
"statecode": 1,
"statuscode": 2
}
//read currect record id
var currentRecordId=formContext.data.entity.getId();
// update the record
await Xrm.WebApi.updateRecord("seven_medicinemaster", currentRecordId, data).then(
function success(result) {
alert("Medicine is Expired Successfully");
formContext.data.refresh();
// perform operations on record update
},
function (error) {
console.log(error.message);
// handle error conditions
}
);
}
else
console.log("Dialog closed using Cancel button or X.");
});
}14. Show Hide Command Button checking current user security role using Enable Rule
This code hides command button depending on the current user role check.
function SecurityCheck(context)
{
var flag=false;
var userRoles=Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext().userSettings;
if(Object.keys(userRoles.roles._collection).length>0)
{
for ( var rolidcollection in userRoles.roles._collection)
{
var currentUserRoles= Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext().userSettings.roles._collection[rolidcollection].name;
if(currentUserRoles.toLowerCase()=="doctor")
{
flag=true;
break;
}
}
}
return flag;
}15. Get and Set Tab Visibility
You can dynamically control the visibility of tabs based on conditions, enhancing the user’s experience by showing only relevant information.
function setTabVisibility(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var fieldValue = formContext.getAttribute("new_fieldname").getValue();
if (fieldValue === "ShowTab") {
formContext.ui.tabs.get("new_tabname").setVisible(true);
} else {
formContext.ui.tabs.get("new_tabname").setVisible(false);
}
}
16. Retrieve User Roles
Sometimes you need to customize the form based on the user’s role. You can retrieve the user’s roles and apply logic accordingly.
function checkUserRole(executionContext) {
var userRoles = Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext().userSettings.roles;
userRoles.forEach(function(role) {
if (role.name === "System Administrator") {
// Perform actions for System Administrators
}
});
}
17. Date Validation
Validating date fields ensures the data integrity and correctness of date-related operations.
function validateDateField(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var startDate = formContext.getAttribute("new_startdate").getValue();
var endDate = formContext.getAttribute("new_enddate").getValue();
if (startDate && endDate && endDate < startDate) {
formContext.getControl("new_enddate").setNotification("End date must be after start date.", "1");
} else {
formContext.getControl("new_enddate").clearNotification("1");
}
}
18. Open a Record in a New Window
You can open a record in a new window for better navigation or specific workflows.
function openRecordInNewWindow(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var entityId = formContext.data.entity.getId();
var entityName = formContext.data.entity.getEntityName();
var url = Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext().getClientUrl() + "/main.aspx?etn=" + entityName + "&id=" + entityId + "&pagetype=entityrecord";
window.open(url, "_blank");
}
19. Enabling/Disabling Fields Based on Conditions
You can enable or disable fields dynamically based on other field values.
function toggleFieldEnablement(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var checkField = formContext.getAttribute("new_checkfield").getValue();
var targetField = formContext.getControl("new_targetfield");
if (checkField === true) {
targetField.setDisabled(false);
} else {
targetField.setDisabled(true);
}
}
20. Handling Subgrid Add New Event
You can execute JavaScript when a user tries to add a new record through a subgrid.
function onSubgridAddNew(executionContext) {
var formContext = executionContext.getFormContext();
var subgrid = formContext.getControl("new_subgrid");
subgrid.addOnLoad(function() {
subgrid.getGrid().getViewSelector().setCurrentView("{00000000-0000-0000-00AA-000010001001}");
});
}
These scenarios illustrate how JavaScript can be utilized in Dataverse/Dynamics 365 CE to create dynamic, user-friendly forms. By incorporating these snippets into your applications, you can significantly enhance functionality and user experience. Always ensure to test thoroughly in a development environment before deploying to production.
Hop this helps.











